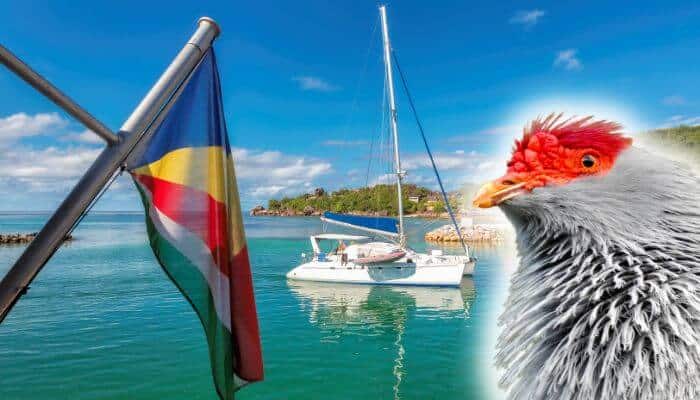
The Seychelles Blue Pigeon is a medium-sized pigeon found only in the woodland areas of the Seychelles archipelago.
This pigeon is most easily recognized by the patch of bright red skin that extends from the forehead to the crown of the pigeon’s head.

Origins of the Seychelles Blue Pigeon
The Seychelles Blue Pigeon (Alectroenas pulcherrimus) is also known as the Seychelles Blue Fruit Dove.
This pigeon species was first described by Italian naturalist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in 1786 and the Alectroenas genus was later defined in 1840 by English naturalist George Robert Gray.
The Mauritius Blue Pigeon was designated as the Alectroenas type species and today there are three species of blue pigeon remaining including the Seychelles Blue Pigeon.
Distribution & Habitat of the Seychelles Blue Pigeon
The Seychelles Blue Pigeon can be found on most of the large and medium islands in Seychelles including Denis, Bird, Aride and Cousin islands.
This pigeon can be found in an estimated area of 7300km and is only found in Seychelles.
Although the species population has not been closely monitored, its numbers have increased since humans stopped hunting Blue Pigeons for food in the late 1970s.
Since then, the Seychelles Blue Pigeon has recolonized a number of islands including Curieuse and Denis in the 1980s, Aride in 1990 and Bird island in 2009.
The preferred habitat of these birds is forests and woodland areas.
Seychelles Blue Pigeons are particularly common in areas with fruiting trees and in montane forests. They can often be seen in the canopy of the trees feeding on fruits.
Closest Columbidae Relatives of the Seychelles Blue Pigeon
In addition to the Seychelles Blue Pigeon, the Alectroenas Genus includes:
Madagascar Blue Pigeon (Alectroenas madagascariensis)
The Madagascar Blue Pigeon is found in Northern and Eastern Madagascar. This pigeon is native to tropical moist lowland forests and tropical or subtropical montane forests.
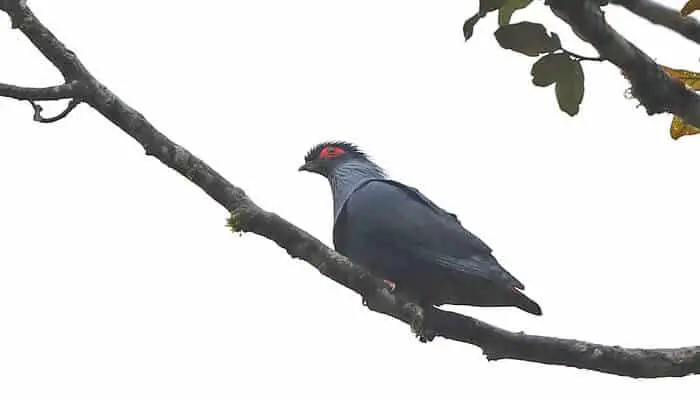

Although not confirmed, the Madagascar Blue Pigeon seems to migrate as they are seen leaving the north of the island during the rainy season to migrate west.
Comoros Blue Pigeon (Alectroenas sganzini)
This species is only found in Comoros and Seychelles, they are often seen in subtropical/ tropical wet lowland forests, montane forests, and mangrove forests.
Comoros Blue Pigeons are usually solitary and are known to fly between the Aldabra islands (flying one way in the morning and back in the evening).
Mauritius Blue Pigeon (Alectroenas nitidissimus) *extinct*
This extinct species was similar to the remaining blue pigeons described above.
Early descriptions of the Mauritius Blue Pigeon date back to the 17th century and in the 18th and 19th centuries stuffed samples were sent to Europe.
These pigeons were pushed to extinction due to deforestation and predation.
Closest Columbidae Relative
The closest Columbidae relative is believed to be the Cloven-feathered Dove (Drepanoptila holosericea).
This dove species is endemic to New Caledonia (also home to the Notou AKA Goliath imperial pigeon) and can be found in forest habitat.
Although there is little known about the Cloven-feathered Doves diet it is known to eat fruit and berries.
Seychelles Blue Pigeon Appearance
This Seychelles Blue Pigeon has a silver-grey head and breast, dark blue wings, tail, and underbody, and a distinctive red patch of bare skin on the head.
They also have a dull yellow bill and dark grey legs.
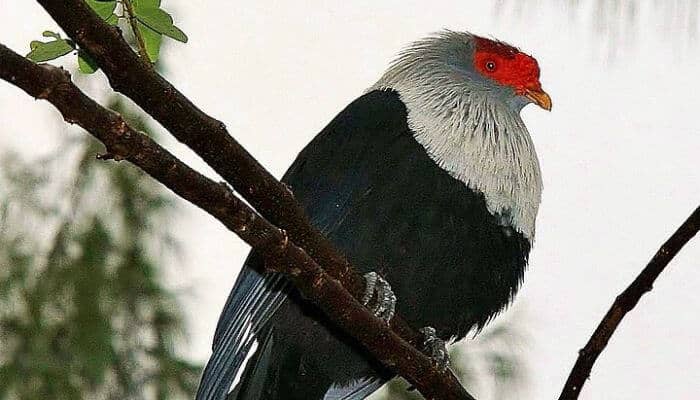

The male and female pigeons look similar although the colors on the females may be slightly duller. The female may also have pale-edged feathers on her body.
The juvenile Seychelles Blue Pigeon looks very different from the adult.
The younger birds have a dark grey head, dark crown feathers with green edges, greenish-brown upperparts with pale yellow fringes, and a pink wattle around the eye.
| Wingspan | Length | Weight | Coloring | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seychelles Blue Pigeon | 38-40cm | 25 – 27cm | 160 – 165g | Dark blue and silver-grey |
| Average Feral Pigeon | 64 – 72 cm | 32 – 37 cm | 300 – 500 g | Bluish gray with some black |
Facts About The Seychelles Blue Pigeon:
- The Seychelles Blue Pigeon is different from other pigeons as their muscular gizzard breaks down seeds to aid digestion, this means their dropping contains no viable seeds.
- This species is known as Pizon Olande in Creole.
- The Seychelles Blue Pigeon is endemic to the Seychelles.
Seychelles Blue Pigeon Conservation
The Blue Pigeons were once shot for food and they were also shot by farmers as an alleged pest.
Since this hunting practice ended in the late 1970s the Blue Pigeon population has increased and is believed to be thriving.
The species is classified as Least Concern on the IUCN Redlist, although the number of mature adults remaining is unknown.
The population of Seychelles Blue Pigeons is suspected to be declining due to habitat destruction and exploitation.
There are conservation sites over this pigeon’s entire range and the species occurs in at least one protected area so although there are no conservation measures specific to the Blue Pigeon they are being protected and conserved thanks to habitat protections.
Seychelles Blue Pigeon Character
There is still a lot to learn about the character and behavior of Seychelles Blue Pigeons, they can be found alone, in pairs, or in small groups of up to 12 birds.
The call of this Blue Pigeon is a short growling note that is made in a long, quick series. The notes are harsh and hoarse but are not heard often as the Seychelles Blue Pigeon is mostly silent.
It is rare to see these birds on the ground, they prefer to spend most of their time high up in fruiting trees.
Blue Pigeons can occasionally be found disorientated on the ground as a result of eating too many overripe/ fermented figs.
These pigeons are cared for by a conservation team for a couple of days and then are released once they have recovered.
Diet
These pigeons eat fruit and seeds including the fruits of ylang ylang and fig trees.
They seem to particularly enjoy figs, wild guavas, and cinnamon berries.
Mating And Breeding Seychelles Blue Pigeons
The female Seychelles Blue Pigeon builds a nest using sticks, the twig nest platform is situated 20-66 feet up a tree.
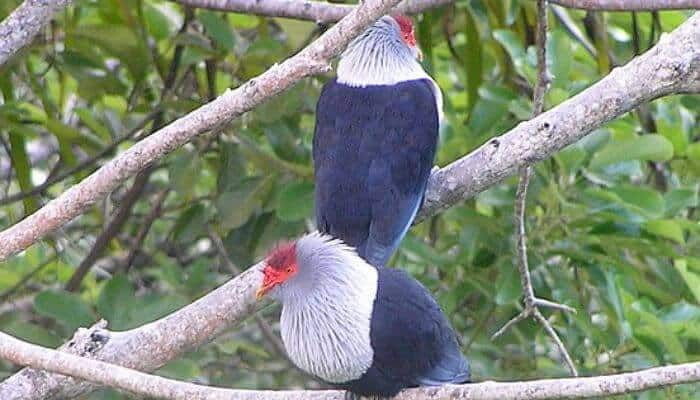

The female will usually lay one egg, although two eggs are occasionally laid.
The egg is incubated for around 28 days and the chick will fledge at about 21 days.
When courting, these pigeons fly above the tree canopy and then plummet towards the ground with their wings held forward and downward.
This behavior may be repeated before the pigeon lands in a tree.
The male pigeon will bow and coo to the female, showing off their plume feathers while strutting. The male will also turn their head 180-degrees and back again when strutting and trying to attract the female.
During courtship, males may be aggressive towards each other as they try to impress the female Blue Pigeons.
Although breeding can happen throughout the year, the Seychelles Blue Pigeons usually breed between October and April.
Caring for Seychelles Blue Pigeons
Seychelles Blue Pigeons are a wild pigeon species and are not suitable for domestication.
As the Seychelles Blue Pigeon population is believed to be declining due to habitat destruction the best thing you can do to help care for this species is to support conservation efforts and respect the habitats that these birds live in.
